Personally it seems Small Language Models fix local workflows faster than giant cloud AI#SmallLanguageModels #ITAutomation
Quick Video Breakdown: This Blog Article
This video clearly explains this blog article.
Even if you don’t have time to read the text, you can quickly grasp the key points through this video. Please check it out!
If you find this video helpful, please follow the YouTube channel “AIMindUpdate,” which delivers daily AI news.
https://www.youtube.com/@AIMindUpdate
Read this article in your native language (10+ supported) 👉
[Read in your language]
Unlocking Efficiency: A Small Language Model Blueprint for IT and HR Automation
👍 Recommended For: IT Managers seeking workflow optimization, HR Executives focused on employee productivity, Tech Decision-Makers evaluating AI ROI
John: Alright, folks, let’s cut through the AI hype machine. We’ve all seen the buzz about massive language models sucking up cloud budgets like a vacuum on steroids. But here’s the real talk: in enterprise IT and HR, the real bottlenecks aren’t solved by throwing more compute at the problem. Ticket queues are exploding, approvals are bogged down in bureaucracy, and your teams are drowning in repetitive drudgery. Enter small language models (SLMs) – lean, mean automation machines that deliver speed, cost savings, and serious ROI without the LLM drama. Drawing from InfoWorld’s blueprint, we’re diving into how SLMs can transform your operations.
Lila: Exactly, John. If you’re a business leader staring at escalating IT costs or HR inefficiencies, this isn’t just another tech trend – it’s a practical fix. Imagine slashing ticket handling time by half while keeping data secure on-prem. We’ll break it down step by step, starting simple and getting into the nuts and bolts.
The “Before” State: Traditional Pain Points in IT and HR
Before SLMs entered the scene, IT and HR automation relied on rigid rule-based systems or bloated large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or PaLM. Think of traditional setups as clunky assembly lines from the industrial age: manual ticket sorting in IT meant helpdesk teams sifting through endless emails, often leading to delays and errors. In HR, processes like onboarding or leave approvals involved outdated workflows – spreadsheets, legacy software, and human oversight that scaled poorly.
The pain was real. According to recent industry reports, 40% of IT leaders report ticket backlogs as a major stressor, while HR teams waste hours on routine queries. Costs ballooned with LLMs, where inference alone could rack up thousands in cloud bills for high-volume tasks. And security? Forget it – sending sensitive data to external APIs was a compliance nightmare. This “before” state left organizations reactive, inefficient, and vulnerable to burnout.
Contrast that with SLMs: compact models like Phi-3 or Llama 3.1-8B, fine-tuned for specific domains. They’re not trying to be all-knowing oracles; they’re specialized tools that automate the mundane, freeing your teams for high-value work.
Core Mechanism: How SLMs Power Automation
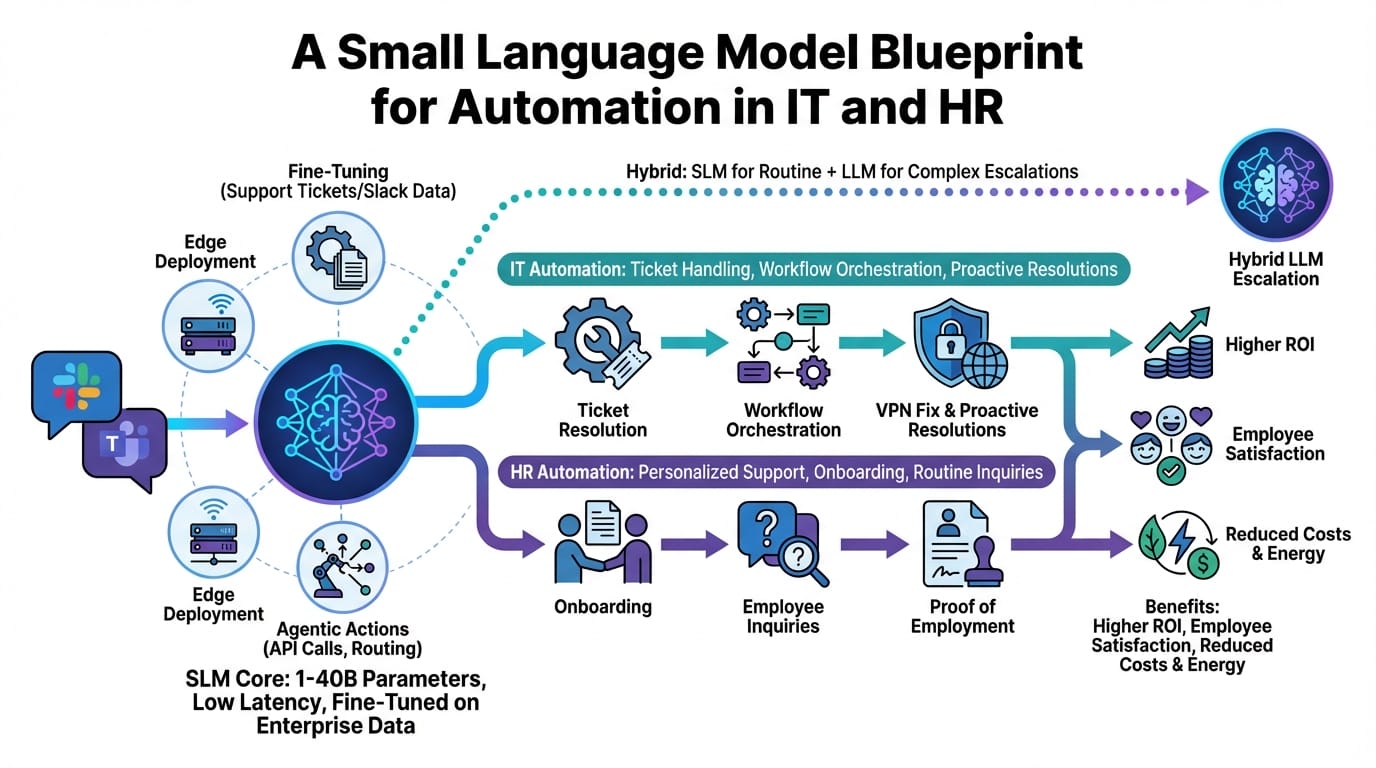
John: Let’s get executive-level on this. SLMs work by distilling the essence of larger models into smaller, efficient packages – often under 10 billion parameters. Using techniques like quantization (shrinking model size for faster runtime) and fine-tuning on domain-specific data, they handle tasks with precision. For IT and HR, the blueprint involves deploying SLMs via open-source frameworks like Hugging Face Transformers or ONNX Runtime for edge inference.
Structurally, it’s about a hybrid setup: an SLM acts as the first-line responder, classifying and routing tickets using natural language understanding. If it’s a simple query – say, resetting a password – the SLM automates it instantly. For complex cases, it escalates to an LLM like Llama 3.1, but only when needed, slashing costs by 70-90% per recent benchmarks from MIT CSAIL.
Lila: To make it intuitive, think of SLMs as the efficient sous-chef in a busy kitchen. They prep the basics quickly and cheaply, while the head chef (LLM) steps in for gourmet flair. This structured reasoning – prompt chaining and tool-calling – ensures accuracy without overkill.
[Important Insight] The key trade-off? SLMs sacrifice some generalization for speed and cost, but in controlled environments like IT/HR, that’s a win – delivering 5-10x faster responses and edge deployment for data privacy.
Real-World Use Cases: SLMs in Action
Let’s ground this in concrete scenarios, pulling from enterprise examples like those in InfoWorld and Harvard Business Review.
1. **IT Ticket Routing and Resolution:** Picture a mid-sized tech firm with a flooded helpdesk. An SLM fine-tuned on historical tickets (using datasets from sources like GLUE or custom enterprise logs) automatically categorizes incoming requests via Slack integrations. For “password reset,” it triggers a script instantly, reducing resolution time from hours to minutes. Outcome: 50% drop in open tickets, boosting team morale and ROI through saved labor hours.
2. **HR Query Handling and Approvals:** In a global HR department, employees bombard the team with policy questions. Deploy an SLM like Microsoft’s Phi-3, integrated with tools like Salesforce or Microsoft Teams. It answers FAQs on benefits or leave policies accurately, pulling from a vector database (via RAG – retrieval-augmented generation, which fetches relevant info without hallucinating). For approvals, it routes to managers with pre-filled forms, cutting processing time by 40% and ensuring compliance.
3. **Onboarding Automation:** New hires in a growing company face delays in setup. An SLM blueprint automates the pipeline: parsing resumes, generating personalized welcome emails, and even scheduling training via APIs. Using models like Mistral-7B, fine-tuned with LoRA (low-rank adaptation, a efficient way to customize without full retraining), it handles variations in applicant data. Result: Faster ramp-up, lower churn, and measurable cost savings on admin overhead.
These aren’t hypotheticals – companies like those profiled in SemiEngineering are already seeing edge AI benefits, with SLMs running on local hardware for real-time decisions.
Comparison: Old Method vs. New SLM Solution
| Aspect | Old Method (Rule-Based/LLM) | New SLM Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow; manual or high-latency cloud calls | 5-10x faster with edge deployment |
| Cost | High; per-query fees for LLMs | 70-90% savings via efficient models |
| Scalability | Limited; rigid rules break at scale | Highly scalable; fine-tune for domains |
| Security | Risky; data sent to external APIs | On-prem deployment keeps data local |
| ROI | Slow payback; high upfront costs |
John: See? The numbers don’t lie – SLMs flip the script on automation economics.
Conclusion: Next Steps for Implementation
In summary, the SLM blueprint for IT and HR automation isn’t about chasing AI trends; it’s about solving real business challenges with pragmatic tech. By leveraging models like Llama 3.1 or Phi-3, you achieve speed, cost efficiency, and strong ROI, all while mitigating risks. The mindset shift? Start small – pilot an SLM on a single workflow, measure baselines, and scale.
Lila: Your next steps: Assess your ticket volume, choose an open-source SLM via Hugging Face, and integrate with tools like Slack. Recent research from MIT suggests collaborative SLM setups could outperform solo LLMs by 20% in accuracy. Dive in – the efficiency gains are waiting.
References & Further Reading
- A small language model blueprint for automation in IT and HR | InfoWorld
- Enabling small language models to solve complex reasoning tasks | MIT News
- The Case for Using Small Language Models | Harvard Business Review
- Small language models and open source are transforming AI | InfoWorld
