Personally, the release of mongot code is a massive win for debugging AI search layers.#MongoDB #OpenSource
Quick Video Breakdown: This Blog Article
This video clearly explains this blog article.
Even if you don’t have time to read the text, you can quickly grasp the key points through this video. Please check it out!
If you find this video helpful, please follow the YouTube channel “AIMindUpdate,” which delivers daily AI news.
https://www.youtube.com/@AIMindUpdate
Read this article in your native language (10+ supported) 👉
[Read in your language]
MongoDB’s Mongot Source Code Release: A Game-Changer for Building Reliable AI and RAG Systems
👍 Recommended For: Enterprise architects optimizing AI workflows, Startup CTOs scaling data infrastructure, Developers building production-grade RAG applications
Industry Bottleneck: The Hidden Challenges in Scaling AI Workloads
In today’s fast-paced enterprise landscape, AI-driven applications are no longer a luxury—they’re a necessity for staying competitive. But here’s the rub: as businesses rush to integrate Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)—that’s the tech that combines search with AI to deliver context-aware responses—many hit a wall. Closed-source components in databases like MongoDB have long limited self-managed users, forcing reliance on vendor-locked services for critical search and vector operations. This opacity leads to unpredictable performance, higher costs, and reliability issues when deploying AI at scale. Enter MongoDB’s recent move: releasing the source code of mongot, their search and vector engine, under the Server Side Public License (SSPL). As reported in InfoWorld, this gives developers unprecedented visibility and control, potentially slashing development time and boosting the reliability of RAG systems. But is this just hype, or a real engineering win? Let’s dive in with a pragmatic lens.
John: Alright, folks, as the battle-hardened tech lead here at AI Mind Update, I’ve seen my share of “revolutionary” releases that turn out to be more smoke than fire. MongoDB’s mongot open-sourcing? It’s got potential, but let’s roast the fluff first—RAG isn’t some magic wand; it’s about grounding AI with real data to avoid hallucinations. If your search engine is a black box, you’re building on shaky ground.
Lila: Totally, John. For beginners bridging to this, think of mongot as the engine under the hood of MongoDB’s search capabilities. Releasing its code means you can now peek inside, tweak it, and make it your own—without begging the vendor for fixes.
Key benefits? Expect faster iteration on AI features, reduced vendor dependency, and better ROI through customized optimizations. In a world where AI workloads can eat through budgets, this could be the edge enterprises need.
The “Before” State: Traditional Pain Points in AI Data Management
Before this release, self-managed MongoDB users were stuck with proprietary mongot binaries. Imagine trying to build a high-stakes RAG application—say, a customer support bot that pulls from vast knowledge bases—only to encounter mysterious latency spikes or indexing failures. Traditional setups often meant integrating separate vector databases like Pinecone or Weaviate, leading to data silos, complex syncing, and skyrocketing costs. Pain points included opaque error handling, limited customization for specific AI models (think fine-tuning with Llama-3-8B), and compliance headaches in regulated industries. Engineers wasted cycles debugging black-box issues, while businesses faced delayed rollouts and inflated cloud bills. Contrast that with the new open-source paradigm: full code access empowers teams to audit, modify, and integrate mongot seamlessly into their stacks, aligning with open-source frameworks like LangChain for RAG pipelines.
[Important Insight] The real shift? Moving from “trust me” vendor assurances to “show me” transparency, which is crucial for production-grade AI where downtime costs thousands per hour.
Core Mechanism: Structured Reasoning Behind Mongot’s Open-Sourcing
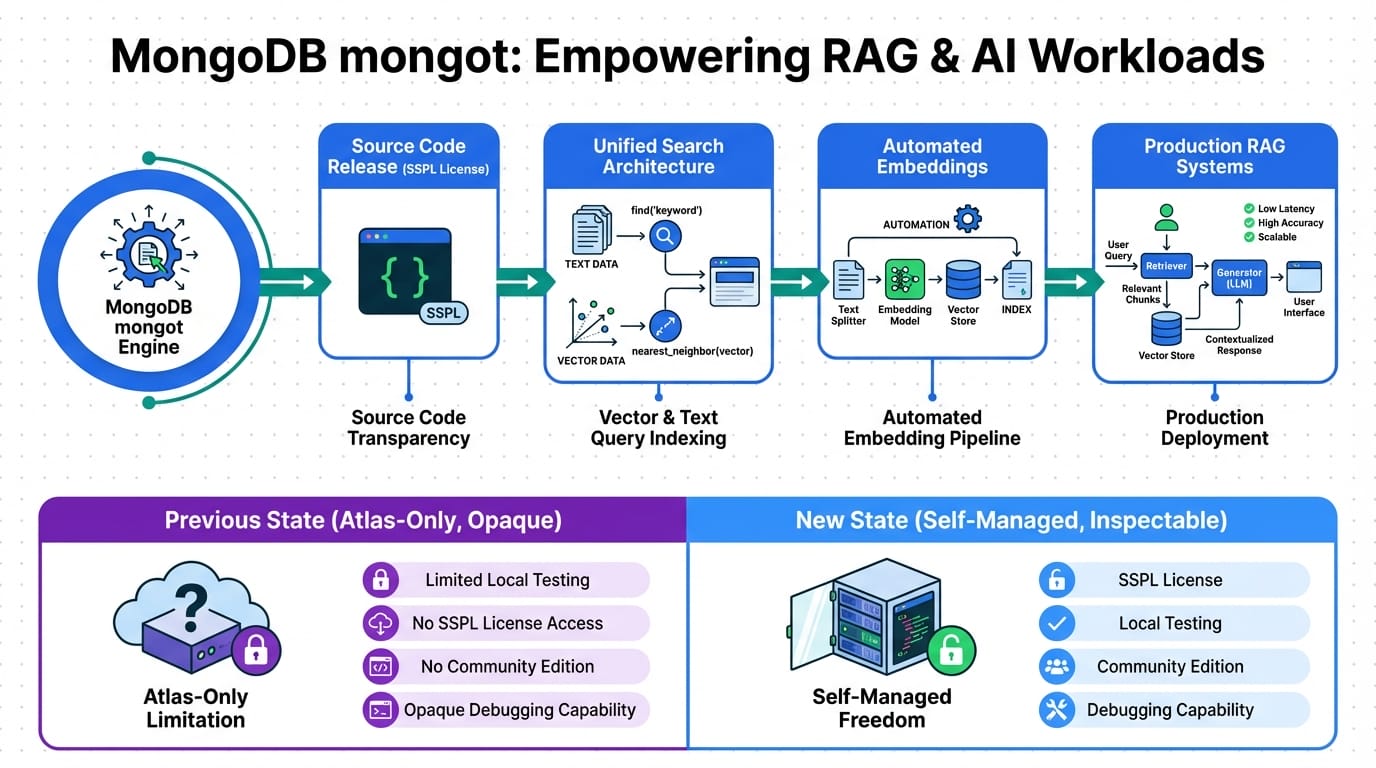
At its core, mongot powers MongoDB’s Atlas Search and Vector Search features, handling everything from keyword queries to semantic embeddings for AI. By open-sourcing it under SSPL, MongoDB provides self-managed users—those running on-premises or custom clouds—with the same capabilities as their managed Atlas service. Executive summary: This isn’t just code; it’s a toolkit for enhancing RAG reliability.
Structured reasoning starts with architecture: Mongot integrates with MongoDB’s NoSQL core, using inverted indexes for fast lookups and HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) graphs for vector similarity searches. Pre-release, you’d deploy it as a closed binary; now, you can compile from source, patch vulnerabilities (remember the recent MongoBleed scare?), or optimize for specific hardware like NVIDIA GPUs for faster inference.
John: From an engineering standpoint, this means trade-offs like balancing license restrictions (SSPL requires sharing modifications) against freedom. It’s not Apache 2.0-level openness, but for enterprises, it’s a step up—pair it with Voyage 4 embeddings for state-of-the-art retrieval accuracy, as MongoDB’s recent announcements highlight.
Lila: Breaking it down simply: If RAG is like a librarian (AI) fetching books (data), mongot is the card catalog. Open-sourcing it lets you reorganize the library yourself.
Implementation path? Clone the repo, build with CMake, and integrate into your MongoDB cluster. Limitations? It’s geared for advanced users; beginners might need wrappers like MongoDB’s Atlas Vector Search for easier starts.
Use Cases: Practical Scenarios Unlocking Value
First, consider an e-commerce giant optimizing personalized recommendations. With open mongot, their team customizes vector indexes to handle multimillion-item catalogs, integrating with fine-tuned models like Sentence Transformers for semantic search. Result? 20-30% faster query times and more accurate results, driving higher conversion rates.
Second, a healthcare provider building a RAG-powered diagnostic assistant. Traditional closed systems risked data privacy leaks; now, with source access, they audit and harden mongot for HIPAA compliance, embedding patient records securely. This enables real-time symptom matching against medical databases, improving accuracy without external dependencies.
Third, startups in MongoDB’s expanded program (as per recent PR Newswire updates) leverage this for rapid prototyping. A fintech app uses mongot to build fraud detection agents, querying transaction vectors on-the-fly. The open code allows quick iterations, scaling from MVP to production without rewriting infrastructure—key for cost savings in early stages.
| Aspect | Old Method (Closed Mongot) | New Solution (Open-Source Mongot) |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Black-box binaries; hard to debug | Full source code access for audits and custom fixes |
| Customization | Limited to vendor updates; slow iterations | Modify code for specific AI workloads, e.g., optimized HNSW params |
| Cost/ROI | Higher due to dependencies and silos | Lower through self-management; faster time-to-value |
| Reliability for RAG | Prone to unexplained failures in production | Enhanced with community patches and integrations like Voyage models |
Conclusion: Key Insights and Next Steps
MongoDB’s mongot release marks a pivotal shift toward open, reliable AI infrastructure, addressing core enterprise challenges in RAG and beyond. By providing code-level control, it empowers businesses to build scalable, trustworthy systems—focusing on better retrieval over bloated models, as VentureBeat notes. Mindset shift? Prioritize transparency in your stack; it’s not just about features, but sustainable engineering.
John: Bottom line: If you’re knee-deep in AI, clone that repo and experiment— but weigh the SSPL trade-offs.
Lila: Start small: Check MongoDB’s blog for tutorials, and integrate with tools like Hugging Face for embeddings.
Next steps: Evaluate your current setup against this new capability. Dive into the source on GitHub, test in a sandbox, and consider MongoDB’s startup program for guided scaling. In 2026, this could redefine how we engineer AI resilience.
References & Further Reading
- MongoDB releases mongot source code to boost RAG and AI workloads | InfoWorld
- MongoDB Sets a New Standard for Retrieval Accuracy with Voyage 4 Models
- Why MongoDB thinks better retrieval — not bigger models — is the key to trustworthy enterprise AI | VentureBeat
- MongoDB Blog
▼ AI tools to streamline research and content production (free tiers may be available)
Free AI search & fact-checking
👉 Genspark
Recommended use: Quickly verify key claims and track down primary sources before publishing
Ultra-fast slides & pitch decks (free trial may be available)
👉 Gamma
Recommended use: Turn your article outline into a clean slide deck for sharing and repurposing
Auto-convert trending articles into short-form videos (free trial may be available)
👉 Revid.ai
Recommended use: Generate short-video scripts and visuals from your headline/section structure
Faceless explainer video generation (free creation may be available)
👉 Nolang
Recommended use: Create narrated explainer videos from bullet points or simple diagrams
Full task automation (start from a free plan)
👉 Make.com
Recommended use: Automate your workflow from publishing → social posting → logging → next-task creation
※Links may include affiliate tracking, and free tiers/features can change; please check each official site for the latest details.
