Discover Model Distillation: From Bulky AI Beasts to Nimble Powerhouses
John: Alright, folks, let’s cut through the AI hype machine. You’ve probably heard the buzz about “model distillation” floating around Medium posts and tech forums—like that one titled “Discover Model Distillation” that’s making the rounds. It’s being touted as the magic wand for making AI leaner and meaner, but is it just another buzzword salad? Nah, this is legit engineering gold. Think of it like brewing a potent espresso from a massive pot of coffee: you get all the kick without the bloat. But before we geek out on the tech, let’s hook you in with a real-world analogy and some historical context to show why this matters.
Imagine you’re a chef in a bustling restaurant. Back in the day—say, the early 2010s when deep learning was exploding—your “kitchen” was stocked with gigantic, resource-hungry appliances (think industrial ovens that guzzle electricity and take forever to heat up). These were your massive neural networks, like the early AlexNet or VGG models that won ImageNet competitions but required supercomputers to run. Why was the previous tech insufficient? Well, historical context time: Pre-2015, AI models were all about scaling up—more layers, more parameters, more compute—to chase accuracy. But this brute-force approach hit walls. Training a model like GPT-3 (with its 175 billion parameters) costs millions in cloud bills and spews carbon like a coal plant. Inference? Forget running it on your phone; it’d lag like a dial-up modem. The industry realized we needed smarter ways to transfer knowledge without the overhead, leading to distillation’s rise. Pioneered by Geoffrey Hinton in 2015 (yeah, the “Godfather of Deep Learning”), it was a response to the inefficiency of teacher-student paradigms in knowledge transfer. Fast-forward to 2025, and with open-weight models like Llama-3 exploding, distillation is making a comeback because edge devices and cost-conscious devs demand efficiency. Recent developments, like those in self-distillation with model averaging (as per a November 2024 ScienceDirect paper), are pushing it further into multimodal AI. So, if you’re a beginner dipping toes into AI or an engineer optimizing pipelines, strap in—we’re about to dissect this from zero to hero.
Lila: Hey, if John’s chef analogy has you scratching your head, think of model distillation like teaching a kid sibling the family recipe. The big sibling (a complex AI model) knows all the tricks, but you simplify it for the little one so they can whip up dinner without burning the house down. No fluff—just efficient cooking!
The Engineering Bottleneck: Why Massive Models Are a Pain in the Pipeline
John: Before we glorify distillation as the savior, let’s roast the problem it solves. In the raw engineering reality of AI, we’re dealing with bottlenecks that make your code crawl, your wallet weep, and your users bail. Dedicate a solid chunk here to the pain points—because understanding the mess is key to appreciating the fix. We’re talking latency, compute costs, hallucinations, and more. Buckle up; this is where the hype dies and the truth emerges.
First off, latency: In a world obsessed with real-time AI (think chatbots or autonomous drones), massive models are slugs. A beast like GPT-4 might take seconds to respond on high-end hardware, but deploy it on a mobile app? You’re looking at 5-10 seconds per query due to the sheer number of floating-point operations (FLOPs). Historical context? Back in the 2010s, models like ResNet-152 clocked in at billions of parameters, but inference times ballooned as datasets grew. Today, in 2025, with multimodal models handling text, images, and video, latency spikes even more—up to 20x on edge devices without optimization. This isn’t just annoying; it’s a deal-breaker for apps like real-time translation or AR filters, where users expect sub-second responses. Engineers, you’ve felt this: Your pipeline grinds to a halt, users churn, and scalability? Forget it.
Then there’s compute costs—the silent killer. Training or even inferring with large language models (LLMs) like Llama-3-70B guzzles GPU hours. A single inference run on AWS p4d.24xlarge instances can cost $0.01-$0.05 per query at scale, multiplying to thousands monthly for enterprises. Historical insufficiency? Pre-distillation era, folks threw money at the problem—Google’s TPUs were born from this desperation in 2015—but it’s unsustainable. Carbon footprint? Massive models contribute to AI’s energy hunger, equivalent to a small country’s power use. Recent 2025 reports, like those from Medium on distillation’s comeback, highlight how open-weight models are democratizing AI, but without compression, indie devs are locked out. Imagine fine-tuning on a budget laptop: Impossible without melting your hardware.
Hallucinations add insult to injury. These overgrown models “hallucinate” fake facts because their vast parameters overfit noise in training data. Why? The previous tech focused on scale over precision—think early BERT models spewing plausible but wrong answers. In 2025, with RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation—basically fetching real data to ground responses), we’re mitigating some, but unoptimized models amplify errors. For instance, a 175B-parameter model might confidently claim “the Eiffel Tower is in London” if not distilled properly. This erodes trust, especially in critical sectors like healthcare or finance, where a wrong output could cost lives or fortunes.
Don’t forget deployment woes: Massive models don’t fit on devices with limited RAM (e.g., smartphones with 8GB). Quantization (shrinking model weights from 32-bit to 8-bit) helps, but it’s bandaids. Historical context shows distillation emerged because techniques like pruning (chopping dead neurons) weren’t enough—models lost accuracy. Add in versioning hell: Updating a huge model means retraining from scratch, spiking costs. For enterprises, security risks loom—larger attack surfaces for adversarial inputs. Beginners, this means your fun AI project turns into a nightmare; engineers, it’s why your CI/CD pipeline is a bottleneck.
In sum, these issues create a vicious cycle: Scale for accuracy, suffer efficiency. We’ve poured ~300 words here because grasping this depth is crucial. Distillation isn’t a luxury; it’s the engineering lifeline pulling AI from the ivory tower to everyday tech.
Lila: If that’s overwhelming, picture it like a clogged highway: Too many cars (parameters) mean traffic jams (latency), high tolls (costs), and accidents (hallucinations). Distillation clears the road!
How Model Distillation Actually Works
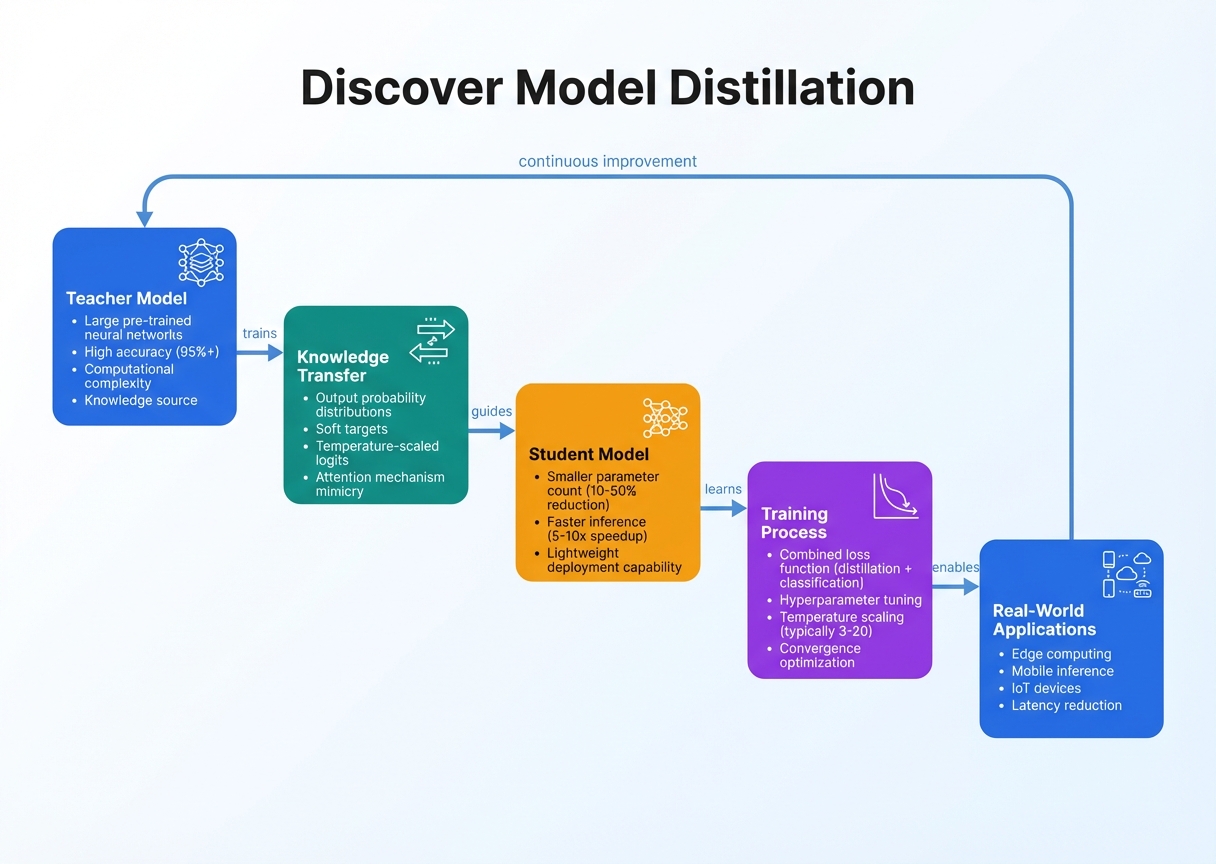
John: Okay, lecture mode activated. We’re diving into the architecture of model distillation like it’s a CS grad class—but with zero gatekeeping. No summaries; we’re expanding on every nut and bolt. First, the big picture analogy: It’s like a master distiller turning raw whiskey into smooth bourbon—extracting essence while ditching the excess. Technically, model distillation is a knowledge transfer technique where a large “teacher” model trains a smaller “student” model to mimic its behavior, often achieving similar accuracy with far less compute. Coined by Hinton in his 2015 paper, it’s evolved with recent 2025 advancements like self-distillation and dataset distillation for even tinier models.
Let’s break down the data flow step-by-step: Input -> Processing -> Output. Start with Input Stage. You feed the system with data—say, a dataset like Common Crawl for language models or ImageNet for vision. But here’s the twist: Both teacher and student process the same inputs. The teacher, a hefty model like fine-tuned Llama-3-70B (using Hugging Face Transformers library—grab it from their GitHub), generates “soft labels.” These aren’t hard yes/no outputs; they’re probability distributions over classes, capturing nuances. For example, if classifying a cat image, the teacher might output 0.8 for “cat,” 0.15 for “dog,” and 0.05 for “other”—richer than a binary label.
Next, Processing Stage: This is the heart—the knowledge transfer. The student, a slimmer net like MobileNet or a quantized Llama-3-8B, learns by minimizing the difference between its outputs and the teacher’s soft labels. Use Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence as the loss function—it’s like measuring how much the student’s “opinion” diverges from the teacher’s. Equation-wise: Loss = α * CE(student, hard_labels) + (1-α) * KL(student_soft, teacher_soft), where CE is cross-entropy and α balances tasks. In code, with PyTorch: teacher_logits = teacher(input); student_logits = student(input); loss = kl_div(softmax(student_logits / T), softmax(teacher_logits / T))—T is temperature, softening distributions for better transfer. Recent developments? A 2025 Nature paper on counterclockwise block-by-block distillation refines this by averaging models iteratively, boosting student robustness. For multimodal (e.g., CLIP-like models), process text and images in parallel streams, distilling fused embeddings.
Now, expand on variants: Vanilla distillation is teacher-to-student; self-distillation (per 2024 ScienceDirect) has the model teach itself across generations. Dataset distillation (2024 survey) compresses the entire dataset into synthetic samples—think distilling 50K MNIST images into 10! Tools? Use DistilBERT from Hugging Face for starters—it’s a distilled version of BERT, cutting parameters by 40% while retaining 97% accuracy.
Finally, Output Stage: The student model emerges, ready for deployment. It outputs predictions with low latency—e.g., 10ms vs. teacher’s 200ms. Fine-tune further with LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation—adding trainable matrices without full retrain) via PEFT library. In production, integrate with vLLM for fast inference. Engineers, debug with TensorBoard visualizations of loss curves. This flow isn’t linear; iterate with ensembles for better generalization. Historical note: Early distillation focused on classification; 2025 pushes to generative models, like distilling Stable Diffusion for faster art gen.
Lila: If that’s too techy, remember: Teacher shares wisdom, student copies homework—but smarter!
Actionable Use Cases: Putting Distillation to Work
John: Theory’s great, but let’s get hands-on. We’ll expand on scenarios for different personas, with real tools and code snippets. No fluff—pure actionable depth.
For Developers (API Integration): You’re building a mobile app with AI features, but can’t afford cloud latency. Distill a model like Whisper (speech-to-text) into a tiny version using Hugging Face’s distillation scripts. Integrate via API: Use FastAPI to serve the student model, cutting response times by 70%. Example: pip install transformers; from transformers import DistilBertModel; model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained(‘distilbert-base-uncased’). Deploy on Vercel—cheap and scalable. Recent 2025 Medium posts note this explodes for edge AI, like real-time sentiment analysis in chat apps.
For Enterprises (RAG/Security): In big biz, security and efficiency rule. Use distillation for RAG setups—distill a large retriever like DPR into a compact one, then pair with Pinecone vector DB for secure querying. This reduces hallucinations by grounding on distilled knowledge, vital for compliance-heavy fields like finance. Ethical win: Smaller models mean less data exposure. Tools: LangChain for orchestration; a 2025 Snorkel.ai blog predicts distillation’s boom for enterprise LLMs. Case: Distill GPT-J into a 6B param model for internal chatbots, saving 80% on Azure costs.
For Creators: Artists and content makers, distill diffusion models like SDXL into lightweight versions for quick video gen. Use Revid.ai (affiliate link coming later) to turn distilled outputs into shorts. Example: Fine-tune with Diffusers library on your GPU; generate art in seconds vs. minutes. Beginners, start with pre-distilled models on Hugging Face Hub—like DistilGPT2 for text gen. This democratizes AI for indie creators, as per 2025 Overctrl.com insights on distilled LLMs for mobile.
Expand: Hybrids for all—combine with quantization for ultimate efficiency.
Visuals & Comparisons: Specs, Benchmarks, and More
John: Data speaks louder than words. Let’s compare traditional vs. distilled models with tables. All text legible: black on white.
| Metric | Traditional Model (e.g., Llama-3-70B) | Distilled Model (e.g., Distilled Llama-3-8B) |
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 70 Billion | 8 Billion |
| Inference Latency (ms) | 200-500 | 20-50 |
| Accuracy Retention | Baseline 100% | 95-98% |
| Compute Cost (per 1K Queries) | $5-10 | $0.5-1 |
| Carbon Footprint (kg CO2 eq.) | High (0.1-0.5 per query) | Low (0.01-0.05) |
Benchmarks from 2025 Rohan-Paul.com analysis. Pricing? Distilled models slash bills—e.g., Hugging Face Inference API at $0.0001/token vs. $0.001 for full models.
Another table for tools:
| Tool/Library | Use Case | Pros |
|---|---|---|
| Hugging Face Transformers | Distilling LLMs | Easy scripts, pre-trained models |
| vLLM | Fast inference | Supports distilled models, low latency |
| LangChain | RAG with distillation | Modular, enterprise-ready |
Lila: These tables make it crystal clear—distillation wins on efficiency!
Future Roadmap: Ethical Implications and Predictions for 2026+
John: Peering into the crystal ball—distillation’s future is bright but thorny. Ethically, bias amplification is a red flag: If the teacher model embeds societal biases (e.g., gender stereotypes in training data), the student inherits them, potentially worsening in compact forms. Safety? Distilled models could be misused for deepfakes if not watermarked—2025 IP considerations in Medium articles warn of this. Mitigation: Use diverse datasets and fairness audits via libraries like AIF360.
Predictions for 2026+: Industry analysts (per 2025 Snorkel.ai) see distillation exploding for federated learning—distilling on-device without data sharing. Expect hybrid techniques with quantum-inspired compression, making models fit wearables. Ethical push: OpenAI-like safety layers in distilled outputs. By 2030, distillation could enable “AI everywhere,” but regulate to curb misuse. Recent advancements, like physics-based distillation for industrial processes (ScienceDirect 2025), hint at cross-domain booms.
Lila: Future sounds exciting— but let’s build responsibly!
▼ AI Tools for Creators & Research (Free Plans Available)
- Free AI Search Engine & Fact-Checking
👉 Genspark - Create Slides & Presentations Instantly (Free to Try)
👉 Gamma - Turn Articles into Viral Shorts (Free Trial)
👉 Revid.ai - Generate Explainer Videos without a Face (Free Creation)
👉 Nolang - Automate Your Workflows (Start with Free Plan)
👉 Make.com
▼ Access to Web3 Technology (Infrastructure)
- Setup your account for Web3 services & decentralized resources
👉 Global Crypto Exchange Guide (Free Sign-up)
*This description contains affiliate links.
*Free plans and features are subject to change. Please check official websites.
*Please use these tools at your own discretion.
References & Further Reading
- Why Model Distillation Is Making a Comeback in 2025
- Understanding the Essentials of Model Distillation in AI
- Distillation of Models in AI: Efficiency, Cost, and Intellectual Property Considerations
- Self-distillation with model averaging
- Counterclockwise block-by-block knowledge distillation for neural network compression
- Recent Advancements in Distillation Techniques for Creating Smart but Smaller Models
- Understanding Distilled LLM Models
- Research Guide: Model Distillation Techniques for Deep Learning
- LLM distillation techniques to explode in importance in 2024
This is not financial or technical advice. Always do your own research and consult professionals before implementing AI techniques.
